Visceral Fat: The Dangers and what you can do
Visceral Fat Dangers in Scottsdale, AZ
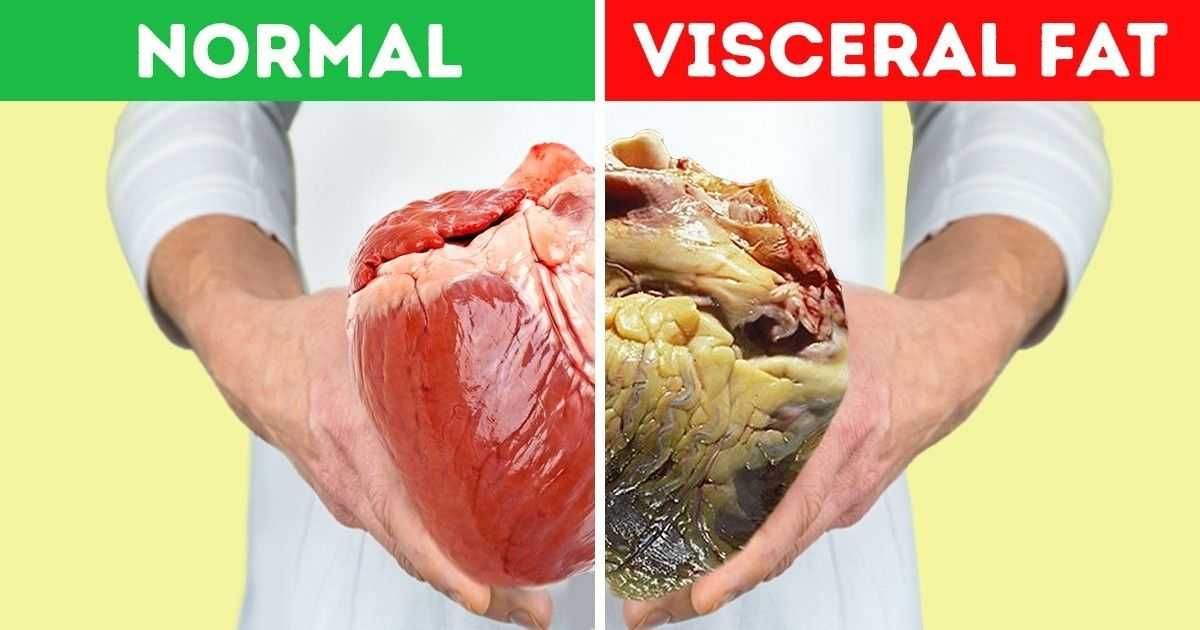
The Dangers of Visceral Fat
Visceral fat, also known as intra-abdominal or deep fat, is a type of fat that is stored deep within the abdominal cavity, surrounding vital organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which is found just beneath the skin, visceral fat is located within the abdominal wall itself.
Visceral fat plays a significant role in regulating various bodily functions, but excessive accumulation of visceral fat can be harmful to health. High levels of visceral fat are associated with an increased risk of several health conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular disease: Visceral fat has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, as it can lead to elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, high blood pressure, and inflammation.
- Type 2 diabetes: Excess visceral fat is closely linked to insulin resistance, a condition where the body's cells do not respond well to insulin. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and, over time, the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic syndrome: Visceral fat is a key component of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of risk factors that increase the likelihood of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These risk factors include abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal lipid levels.
- Fatty liver disease: Visceral fat can contribute to the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition where fat accumulates in the liver, potentially leading to liver damage and inflammation.
- Certain cancers: Some studies have suggested a link between excess visceral fat and an increased risk of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer.
It's important to note that not all fat in the abdominal area is necessarily visceral fat, as there is also subcutaneous fat present. However, excess visceral fat, particularly when combined with other risk factors like a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet, can significantly increase the risk of various health problems. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help reduce visceral fat and improve overall health.
How does Visceral Fat affect Metabolism
Visceral fat can have a significant impact on metabolism, leading to various metabolic changes and increasing the risk of metabolic disorders. Here's how visceral fat affects metabolism:
- Insulin Resistance: One of the key ways visceral fat affects metabolism is by promoting insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels and facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells for energy. Excess visceral fat can disrupt this process by releasing inflammatory substances known as cytokines and free fatty acids. These substances can interfere with insulin's ability to function properly, leading to insulin resistance. When cells become resistant to insulin, it can result in elevated blood sugar levels and, over time, may lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Abnormal Lipid Profile: Visceral fat can also influence lipid metabolism. It tends to release more free fatty acids into the bloodstream, which can contribute to an abnormal lipid profile characterized by elevated levels of triglycerides and lower levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol. This combination is often seen in individuals with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of risk factors associated with heart disease and diabetes.
- Increased Inflammation: Visceral fat is metabolically active and releases inflammatory substances called adipokines. Excess adipokines can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation throughout the body. Inflammation is closely linked to metabolic dysfunction and has been implicated in the development of various metabolic disorders, including insulin resistance, atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and fatty liver disease.
- Altered Hormone Regulation: Visceral fat can disrupt the regulation of hormones involved in appetite and satiety, such as leptin and ghrelin. This disruption can contribute to overeating and weight gain, further exacerbating metabolic issues.
- Increased Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: Due to its influence on insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, inflammation, and hormonal regulation, excess visceral fat is a key component of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that include abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal lipid levels. Individuals with metabolic syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
In summary, visceral fat affects metabolism by promoting insulin resistance, abnormal lipid profiles, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances. These metabolic changes increase the risk of various health conditions, particularly type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Reducing visceral fat through a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, and lifestyle modifications can help improve metabolic health and reduce the associated risks.
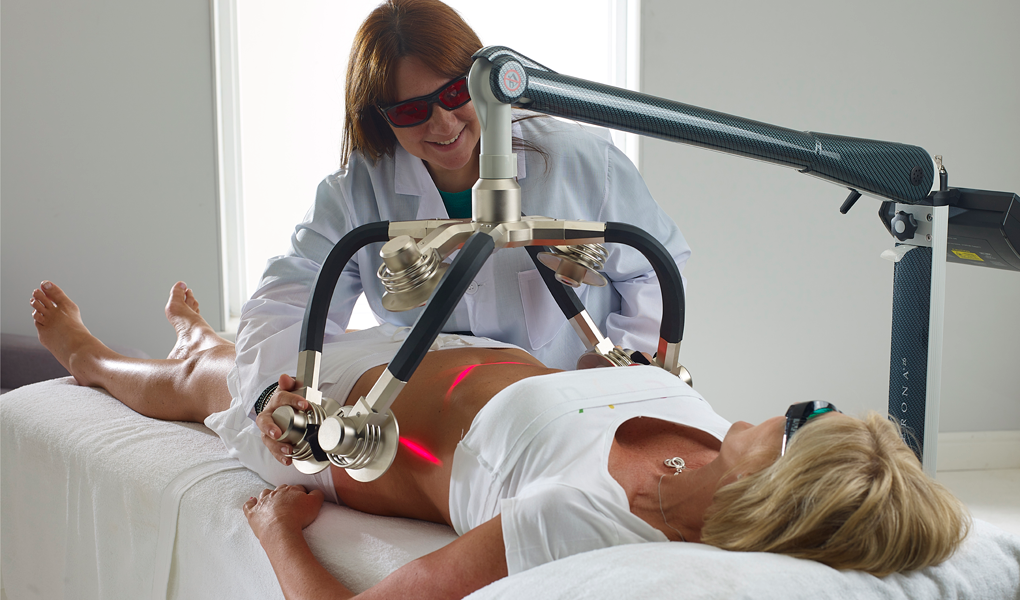
Contact Catalyst Wellness for a consultation to learn more about the Erchonia Cold Laser Therapy and how to reduce Visceral fat cells.